National Report on 2024 Self-Storage Investment
NATIONAL ECONOMY
- The overall outlook in early 2024 is notably more positive in comparison to forecasts made entering last year, as economic indicators continually defied recessionary predictions, despite additional headwinds emerging. The Federal Reserve’s goal of an economic soft landing appears achievable, with most economists anticipating a year of soft, but steady, growth.
- This cautious optimism extends to labor markets. While a slower pace of economic growth will temper hiring, with contractions anticipated in some fields, roughly 1.7 million jobs are still expected to be added nationwide this year. Loosening monetary policy could alleviate some of the financing pressures that businesses are facing, facilitating more hiring in the year’s latter half. Black swan events stemming from geopolitical or climactic currents could disrupt growth, however.
- Despite some temporary deviations from the course, inflation has broadly trended downward over the past two years, taking pressure off businesses and consumers. Still, impacts to global shipping, and potential labor disputes on the horizon, may have inflationary effects. Nevertheless, the economy weathered similar headwinds in 2023 to post a year of solid growth.
CAPITAL MARKETS
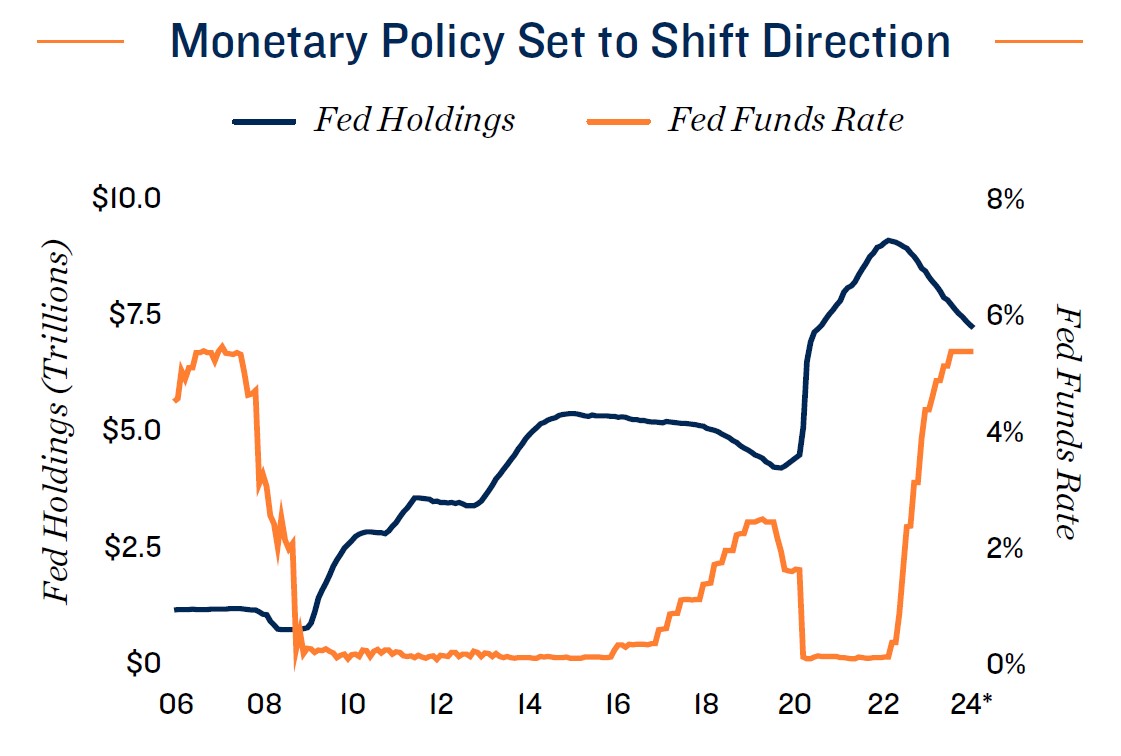
- Following a historical 18-month tightening cycle in which the lower bound of the federal funds rate increased 525 basis points, the Federal Reserve signaled that rates had hit their peak in late
2023. The Fed has indicated that rate cuts will begin later this year. The institution is also continuing to unwind its balance sheet, with the decision regarding how much to decrease holdings to be undertaken at some point in 2024. - The industry’s consistent cashflows have positioned self-storage assets more favorably among lenders than some other major property types. Lenders are more amenable to financing acquisitions in regions noting strong in-migration, though they remain conscious of oversupply risks, conducting more stringent due diligence in areas receiving a large number of new projects.
- Easing rates have already created opportunities for some investors, as falling long-term interest rates have eased borrowing costs in the permanent financing market. If the Federal Reserve
lowers the overnight rate later this year, buyers who have been sidelined could pursue new storage opportunities, supporting further activity in the investment market.
NATIONAL SELF-STORAGE OVERVIEW
- Self-storage vacancy was near pre-pandemic levels in most major metros entering 2024, despite substantial construction during the preceding four years. The absorption of this space
indicates increasing long-run storage demand. Although vacancy will rise on a national basis this year, improving household formation should facilitate a solid backdrop for storage use. - Elevated borrowing rates and materials costs continue to weigh on self-storage development this year, with construction on a downward trend nationwide. However, some Southeastern
locales with strong in-migration remain hotspots for new construction. Developers may also have to contend with sporadic construction moratoriums aimed at curbing new projects. - Rents will be the primary plane of competition among storage operators this year. Many major firms are employing dynamic pricing models that maneuver asking rates to more favorably
meet market demand, while in place rents hold steady. This will aid revenue gains for top operators, despite declining street rates, and put smaller firms at a disadvantage.
INVESTMENT OUTLOOK
- Multiple large-scale mergers and acquisitions headlined the storage sector in 2023, highlighting the increasingly important role that institutional actors have come to play over the past
half-decade. While trades of properties below $10 million declined in 2023 relative to 2019, sales of assets north of that value doubled, despite notable financing headwinds last year. Consolidation could continue as many of the industry’s top operators look to increase marketshare. - A number of third-party management services have arisen in recent years as the sector has matured. Many of these services grant users access to dynamic pricing models, and partnering
with such a firm can ease the financing process. - Long-term migration trends over the past decade — which intensified in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic — have favored Rocky Mountain and Sun Belt metros, where a large share of
investment has shifted as a result. A number of new projects completed since the onset of the health crisis in these areas has greatly increased the options for acquisition in these locales.
ECONOMIC OUTLOOK
Year Ahead Defined by Cautious Optimism and Steady Growth; Potential Headwinds on the Horizon
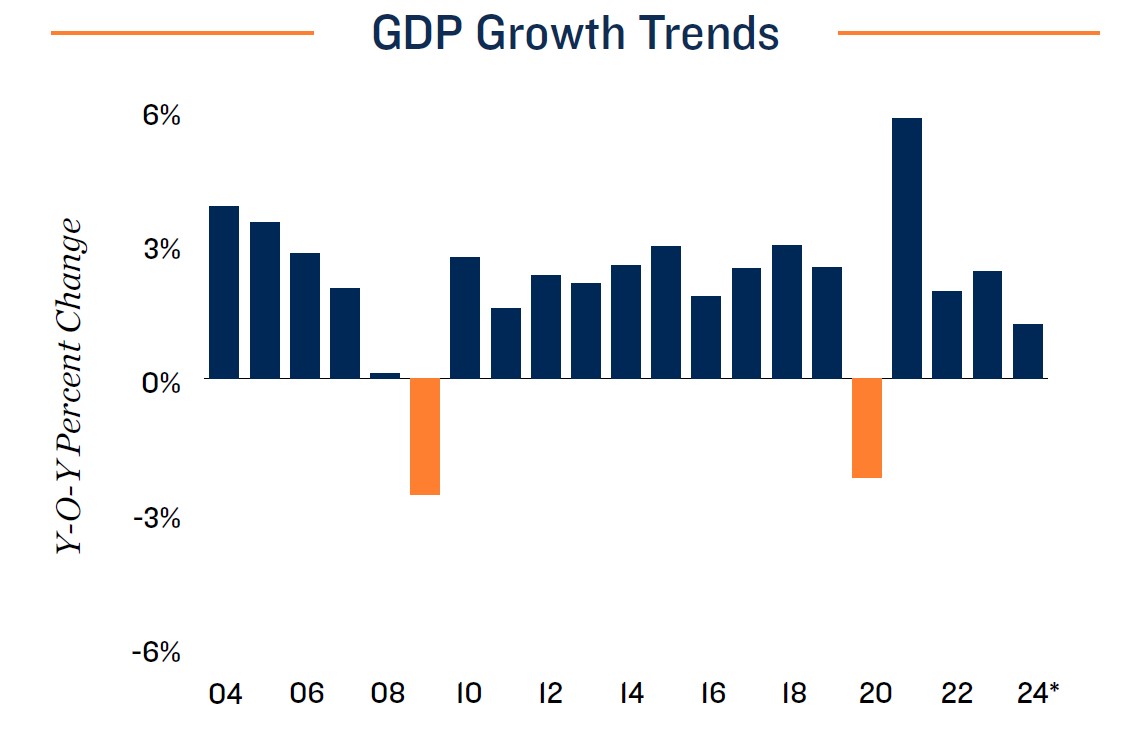
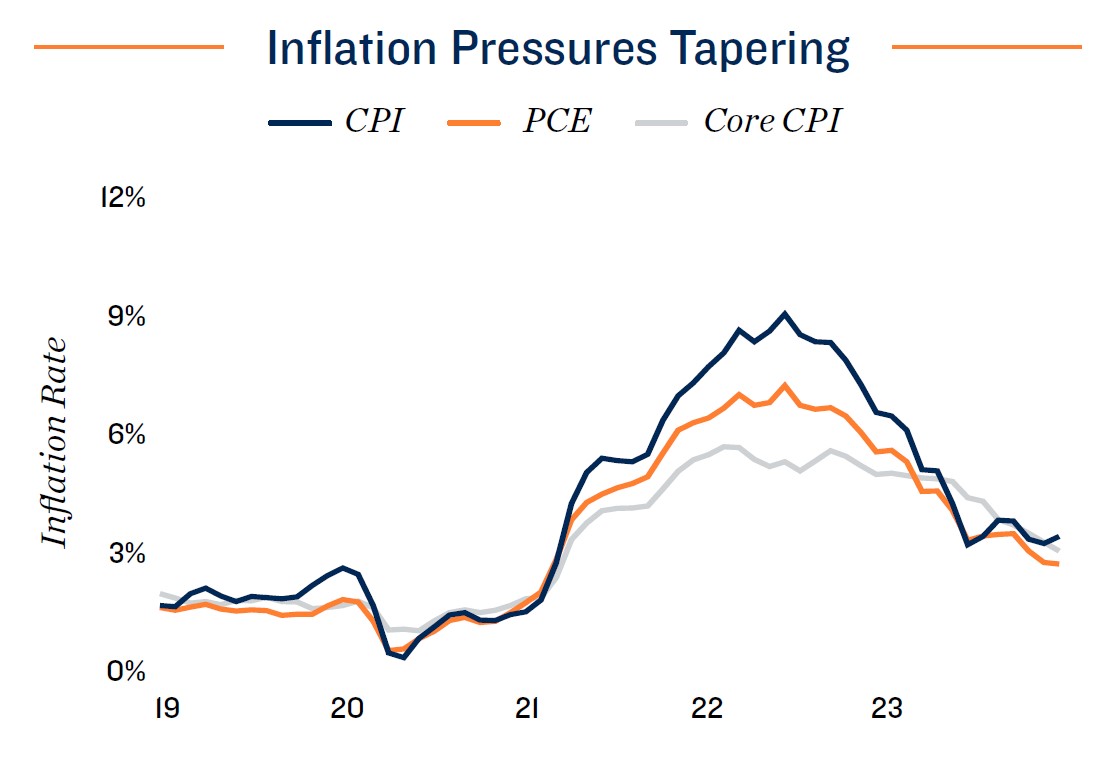
Dominant outlook favors soft landing, but a variety of risks remain. The economy proved more robust than anticipated in 2023, achieving real GDP growth of 2.5 percent despite predictions of a recession. Strong consumer spending has been a major contributor, facilitated by median household wealth that was 36 percent above the pre-pandemic peak, well ahead of elevated inflation. Aggressive action by the Federal Reserve has helped tame price increases, despite exacerbating factors like the Russo-Ukrainian War and the conflict in the Middle East, as well as political gridlock and Congress’ inability to set a budget in a timely manner. After jumping 6.5 percent in 2022, the PCE Index only increased by 2.6 percent last year, not far from the Fed’s target rate. Lessened inflation has substantially bolstered optimism. The Consumer Confidence Index surged to a near two-year high in December, followed by a survey conducted by the National Association for Business Economics in which 91 percent of respondents placed the chance of a near-term recession below 50 percent. While that is a more bullish outlook than last year, downside risks remain. Many shoppers leaned on credit in 2023, driving both total consumer debt and revolving credit debt to record highs. Black swan events could also challenge the generally optimistic outlook for 2024.
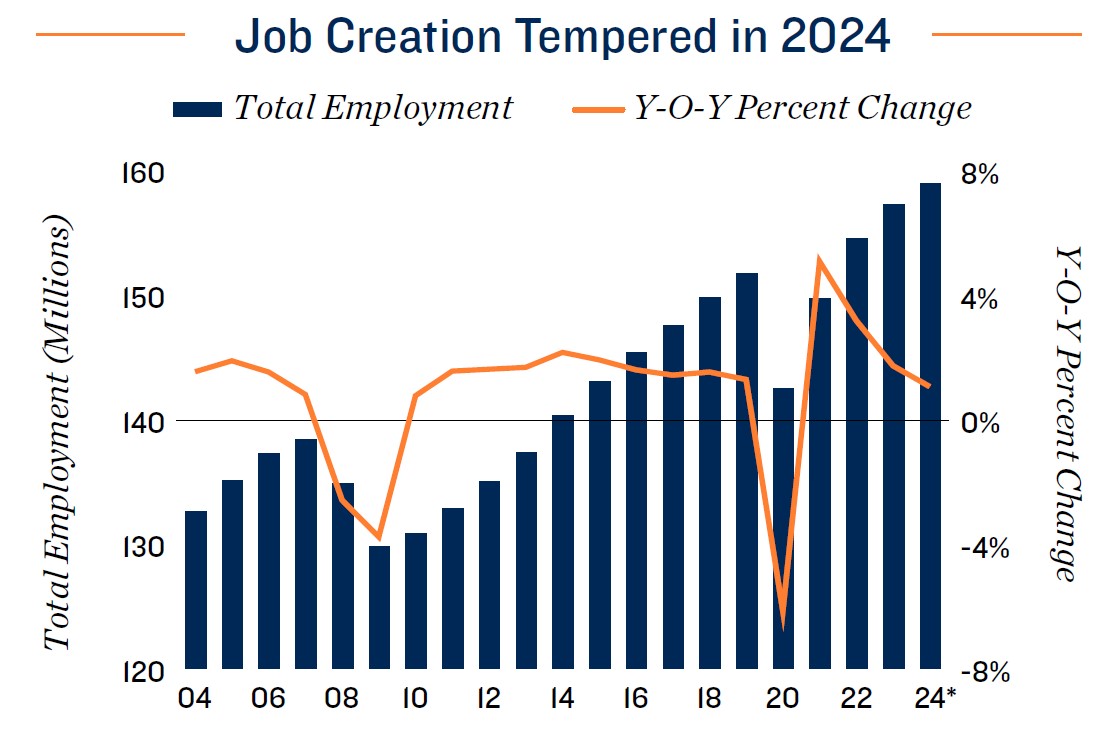
Job additions expected to taper as Fed’s soft landing appears achievable. A historically tight labor market has been another pillar of economic strength, with the nationwide unemployment rate holding in the upper-3 percent range since early 2021. As the pace of economic growth wanes under the weight of elevated interest rates, job
formation will likely continue to slow. An average of nearly 400,000 jobs were added per month throughout 2022, declining to roughly 225,000 last year. That figure is expected to fall further in 2024, with employers anticipated to add less than 150,000 jobs on a monthly average basis. Some fields and markets may experience a period of job loss, with layoffs in the tech sector continuing into early 2024. As inflation aligns more closely with the Fed’s target, however, loosening monetary policy could take some pressure off employers and consumers in the second half of the year.
2024 NATIONAL ECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- Inflation trends toward target. Although it will take some time for the pace of price increases to reach the Fed’s 2 percent annual target, inflationary gauges have consistently trended downward since mid-2022, with both the trailing three- and six month annualized inflation readings coming in below 2 percent. Still, extant hurdles could elongate this process as the year unfolds.
- Threats to global shipping exacerbate uncertainty. A combination of climactic and geopolitical factors have impacted shipping through the Panama and Suez canals, causing some cargo to be rerouted. These types of challenges could slow disinflationary trends as shipping costs rise once again.
- Labor disputes an ongoing risk. High-profile labor disputes have made headlines in recent years, some of which stalled movement through West Coast ports. Similar disruptions are possible this year, as the contract between the International Longshoremen’s Association and U.S. Maritime Alliance is up for renewal in late 2024. Union leaders have already signaled a willingness to strike if negotiations stall.
*Forecast
SELF-STORAGE OVERVIEW
Storage Demand Slowing, but Still Durable;
Rental Rates Becoming Increasingly Fluid
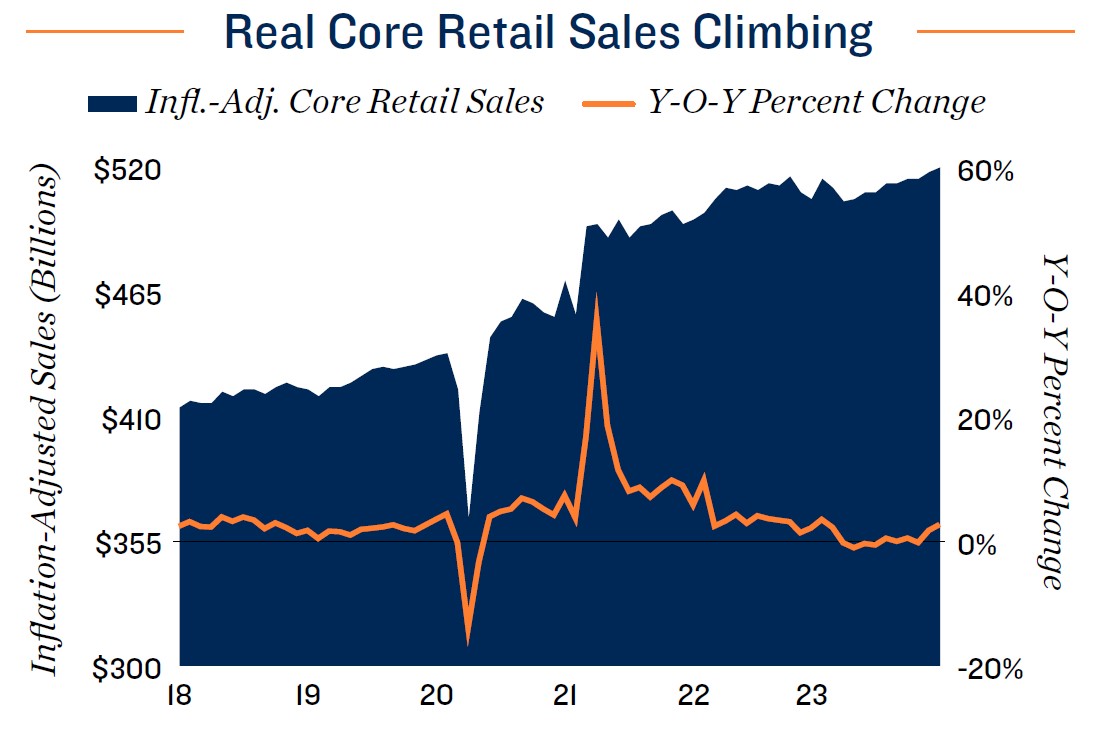
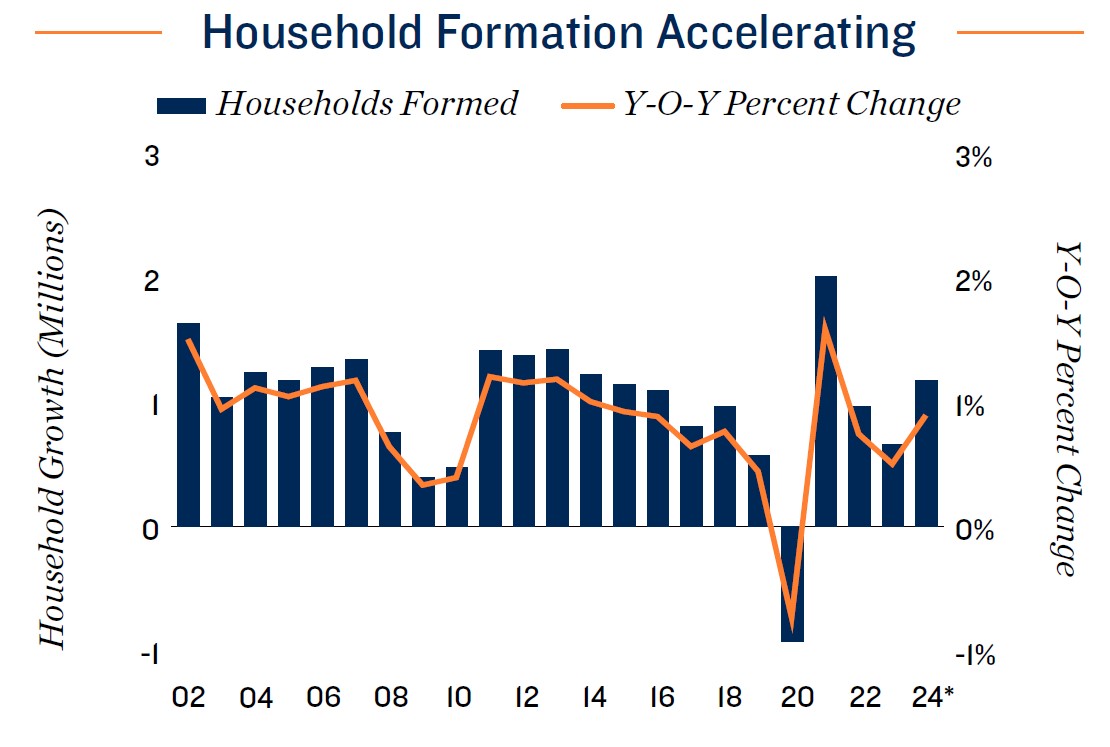
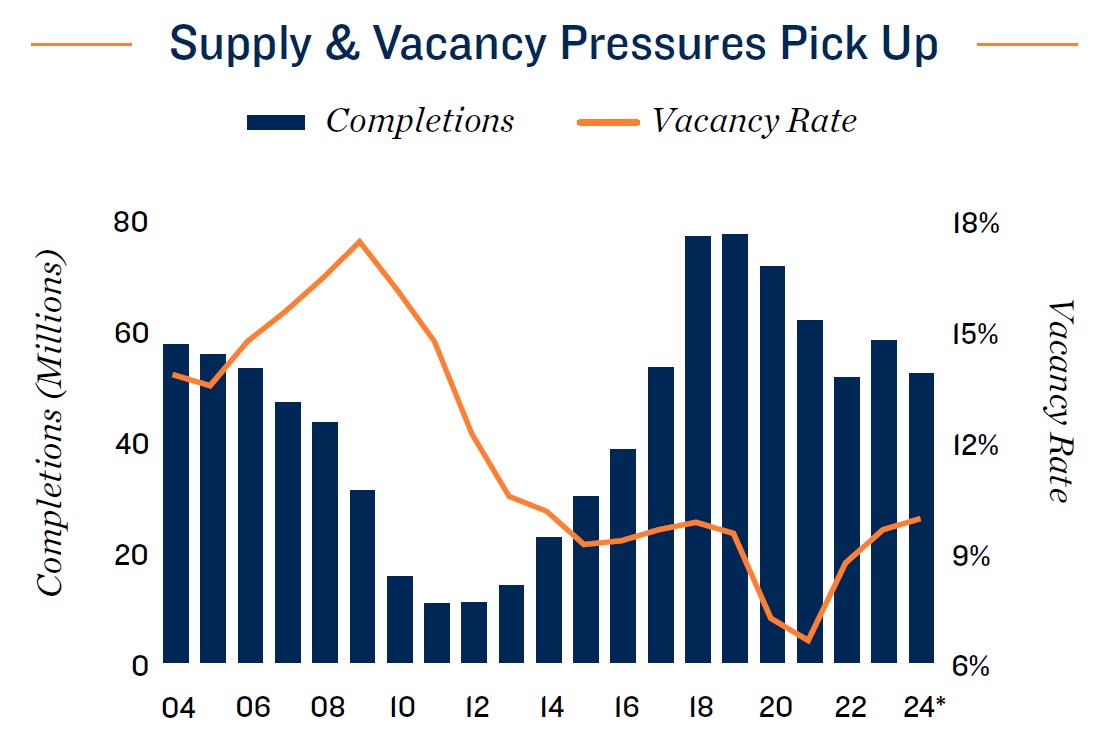
Vacancy holds at pre-pandemic norms, despite supply influx. Following a stretch of historically low vacancy resulting from pandemic lockdowns, self-storage fundamentals were defined by a period of normalization in 2022 and 2023. The national vacancy rate entered 2024 at 9.6 percent, near pre-COVID-19 levels, despite an inventory increase of 13.6 percent, nearly 242 million square feet, during the preceding four years. Despite expectations of increasing household formation this year, the tight housing market could restrain storage space needs, placing upward pressure on vacancy rates in most major metros. The average 30-year fixed-rate residential mortgage was near 7 percent in early 2024, discouraging owners with lower rates from selling and reducing household mobility, a major source of storage demand. On a positive note, loosening monetary policy expected later in the year could stoke the housing market and relieve some of the restraints on home sales, in turn reviving storage space demand.
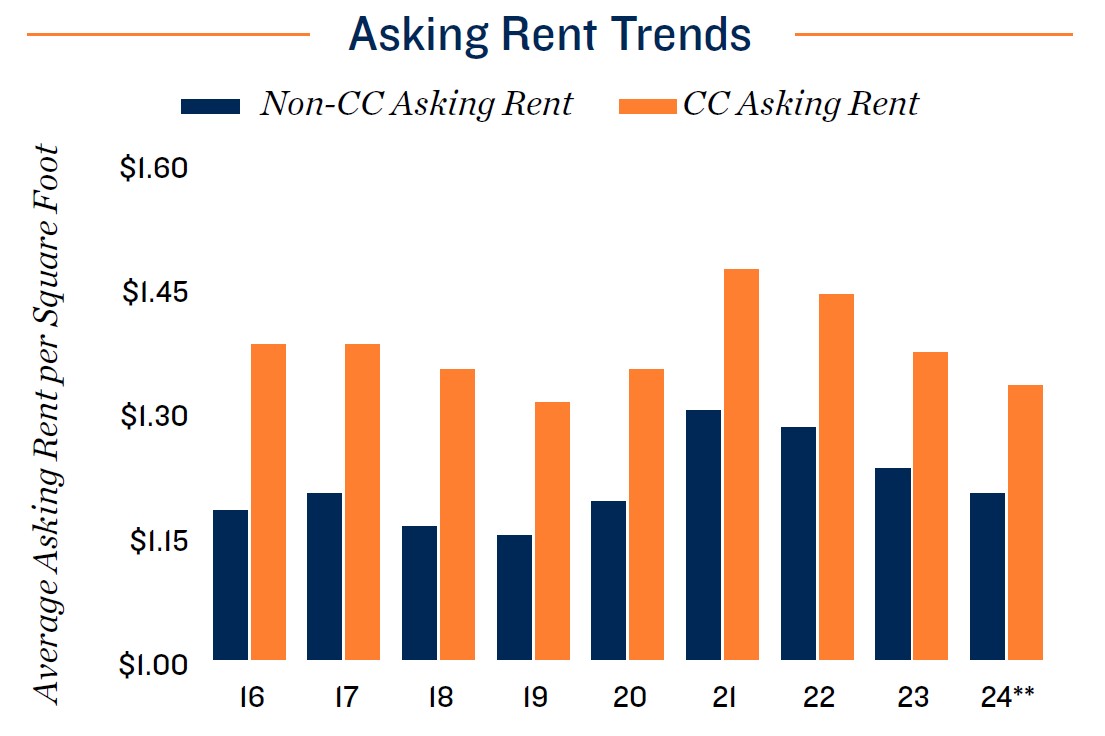
Sector consolidation drives change in street rate dynamics. Since late 2022, the storage industry has been impacted by falling asking rents. While this sparked concerns of oversupply, particularly in markets with active development pipelines, evolving pricing models have played a more significant role. Private owner-operators traditionally dominated the storage business, but as the sector has matured, major firms have acquired nearly 60 percent of net rentable square footage in the U.S., with an outsized presence in major metropolitan areas. As larger operators have increased their market presence, they have started to apply dynamic pricing with low teaser rates to draw in new tenants, followed by subsequent rate increases to ultimately achieve a higher target monthly rent. This has reduced visibility into actual effective rents while putting downward pressure on asking rates. In many cases, this has put some of the smaller private operators at a competitive disadvantage because they may lack the market data and automated systems to replicate the dynamic pricing models.
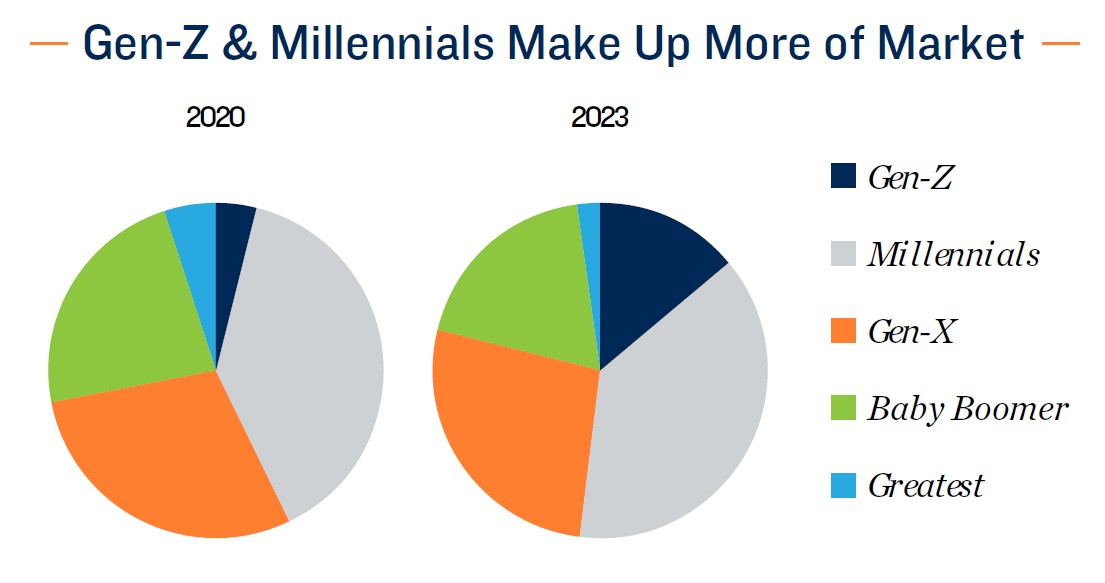
2024 NATIONAL SELF-STORAGE OUTLOOK
- Supply additions taper across most major metros. Elevated construction loan rates and materials costs have weighed on development, with deliveries tapering this year. Investors should, however, remain cautious about the pipeline of facilities that could come online in 2025 and 2026 as the flow of construction capital into self-storage has been on the rise in recent months.
- Local legislation continues to sporadically impact development. Entering 2024, certain municipalities have adopted moratoriums or similar restrictions aimed at limiting the development of self-storage properties. These initiatives are usually limited to specific areas within wider metros.
- REITs largely focus on major metropolitan areas. Although large self-storage REITs are a substantial force in urban and suburban locales, they have yet to branch out to rural areas where their scale, infrastructure and management capabilities deliver a less substantial advantage. As the sector consolidates, the largest operators may seek growth opportunities in smaller markets.
* Forecast for 2024, year-end 2023 vacancy rate estimated
** Forecast
CAPITAL MARKETS
Anticipated Fed Rate Reductions Could Begin to Thaw Lending Climate and Bolster Transaction Activity
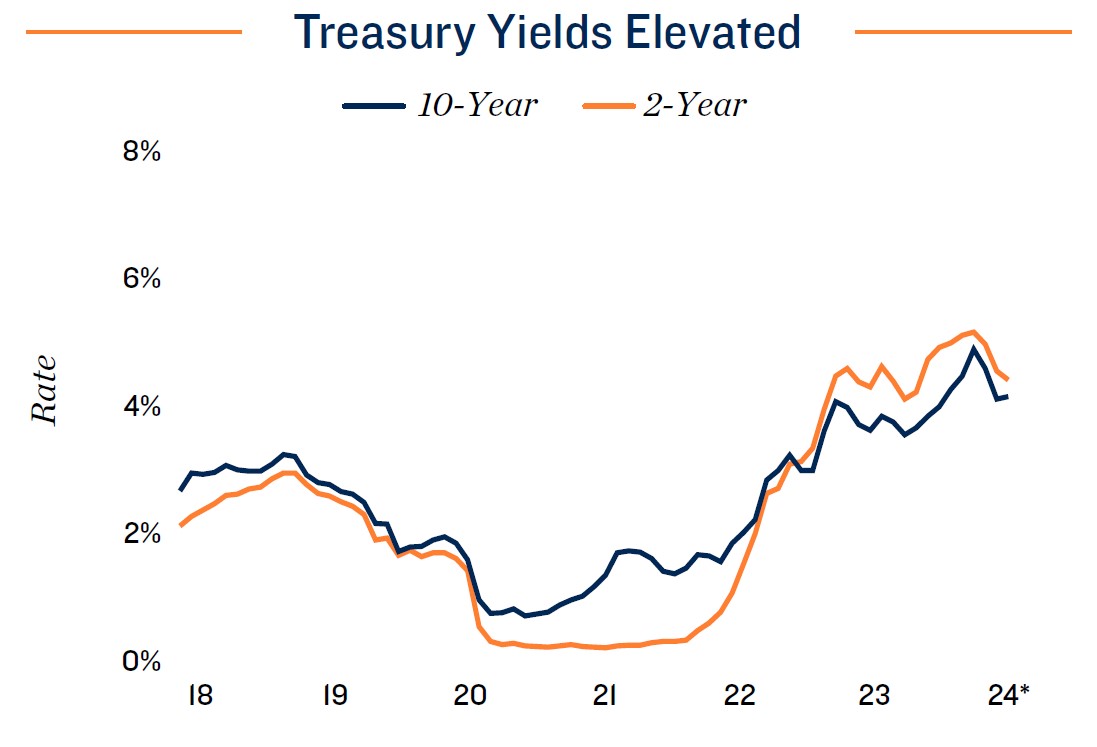
Federal Reserve signals rate cuts ahead. Capital markets were rocked by the Fed’s 18-month tightening cycle that increased the federal funds rate to a lower bound of 5.25 percent. Since then, core PCE inflation, the Federal Reserve’s preferred price gauge, has substantially decreased, ending 2023 at 2.9 percent on an annual basis. After late last year, the FOMC has indicated that rate cuts could potentially start at some point in 2024. The Fed is also continuing to unwind its balance sheet, placing upward pressure on longer-term rates, and has signaled that further decisions regarding how much to decrease holdings will be undertaken later in the year. Although higher borrowing costs have constrained investment sales across property types, including self-storage, capital has continued to accumulate, suggesting that declining interest rates could unlock more of these pent-up funds and bring a share of investors that have been sidelined over the past year to the market.
Lenders focus on experienced owners and regions of stable demand. Although financing acquisitions continue to face significant hurdles, self-storage is among the best positioned commercial property types entering 2024. The industry’s consistent cashflows will continue to be a draw, with lenders amenable to financing trades involving
assets reporting less than 20 percent vacancy. CMBS lenders have continued to pursue loans in the storage industry, though both regional banks and more localized lenders will likely increase activity in 2024 — especially after the Fed begins to reduce rates. Regions with strong in-migration, such as the Sun Belt and select Rocky Mountain metros, will remain most attractive to lenders. On the borrower side, lenders have favored parties with in-depth storage ownership and operating experience. Still, investors new to the sector may be able to leverage existing banking relationships and partnerships with seasoned third-party management services to secure financing.
2024 CAPITAL MARKETS OUTLOOK
- Lending sources vary on asset preference. Although performance is solid across the sector, lenders often focus on a particular niche. CMBS lenders, for example, target REIT portfolios or other trades of multiple high-quality properties. Banks, on the other hand, have generally been more flexible with asset location, size and quality.
- Lenders conscious of oversupply risks. While supply additions are currently on a downward trend nationwide, certain Sun Belt locales continue to note weighty development pipelines. As such, lenders are likely to conduct more stringent due diligence in areas where new projects could saturate the market. Still, these risks are localized, and will not entirely preclude financing in metros with active development.
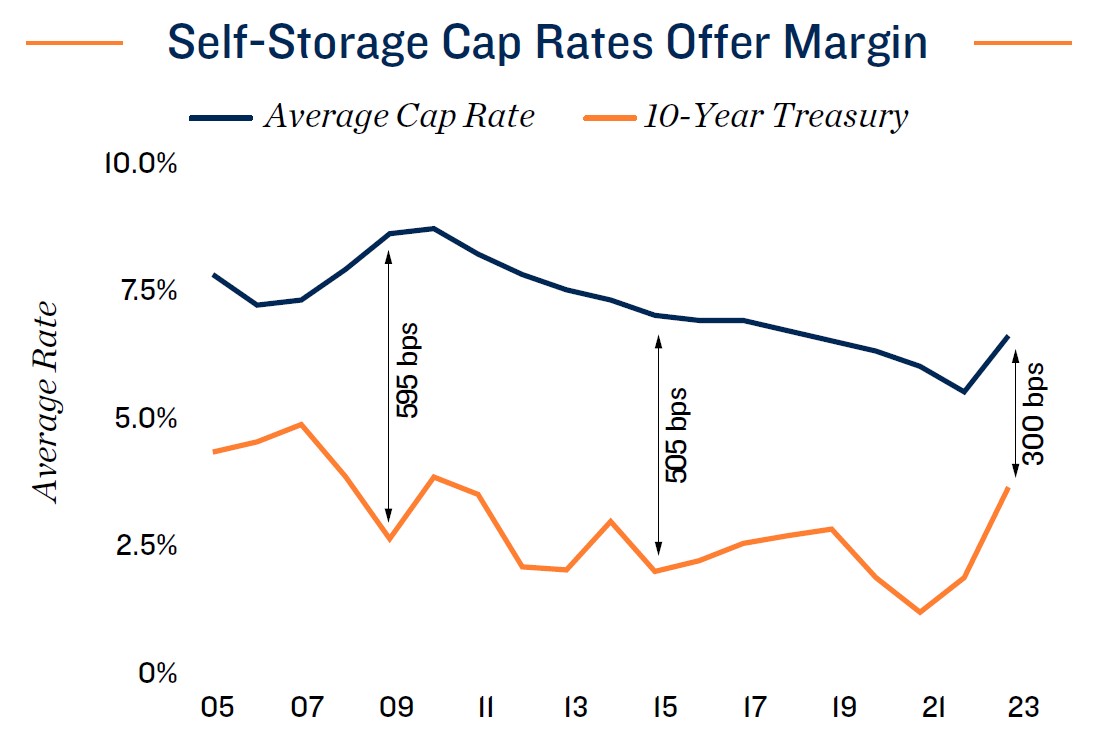
- Easing rate climate beginning to translate to opportunity. In December 2023, 10-year treasury returns fell below 4 percent, translating to lower borrowing costs in the permanent financing market. As of early 2024, storage owners were able to close perm loans in the 6 percent zone as opposed to the 7 percent norm noted late last year.
* Through Jan. 31
SELF-STORAGE INVESTMENT OUTLOOK
Investment Landscape Well-Positioned as Prospect of Loosening Monetary Policy Stokes Investor Demand
REITs drive large, high-quality asset transaction climate. Although financing hurdles have subdued storage transaction velocity following the highs noted in 2021 and 2022, buyer appetites remain considerable. The transaction flow last year, excluding the Extra Space acquisition of Life Storage, was up modestly compared to 2019, but the momentum was not evenly distributed. There were about 7 percent fewer sales of properties priced below $10 million, while the sale of properties above that price point more than doubled. The perception that storage has higher recession tolerance and can provide asymmetrical risk benefits to portfolios has attracted a range of new investors to the sector. Some institutional-grade investors have also begun to add storage to their
portfolio mix, further validating the asset class as a more mainstream property type.
Reduced interest rates could spur storage sector. Should a reduction of the overnight rate by the Federal Reserve lead to lower single-family mortgage rates, it could boost home sales, which have historically aligned with storage space demand. When combined with an anticipated rise of household formations in 2024, this convergence could
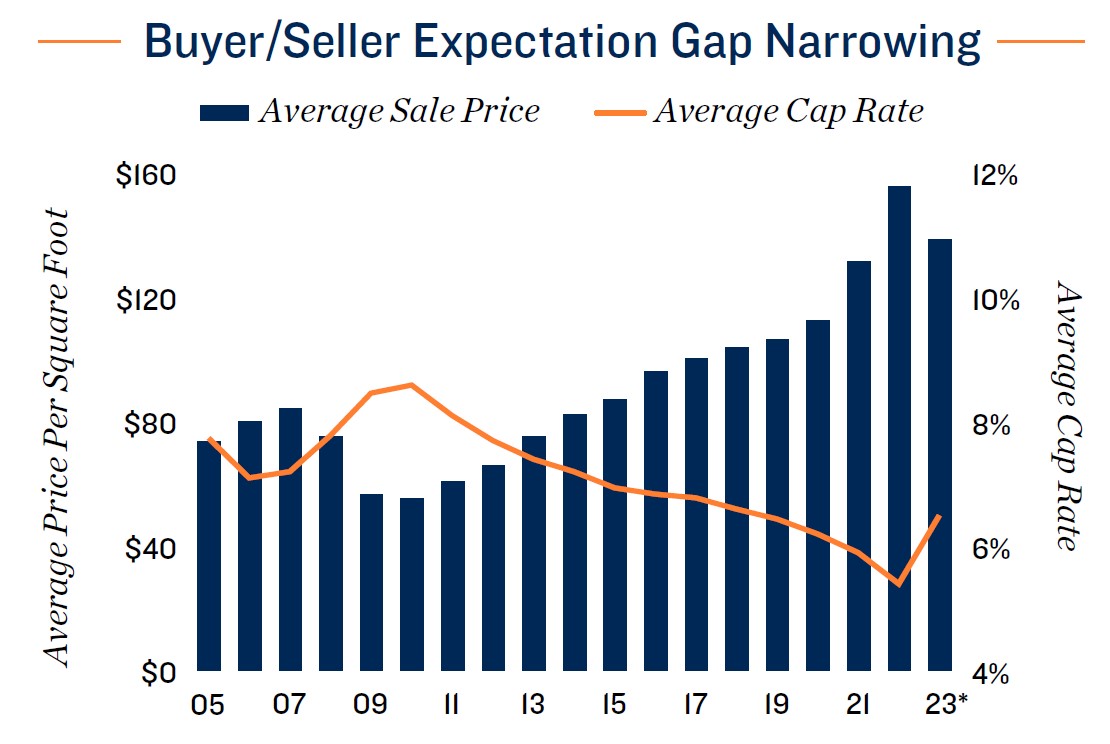
boost storage space demand above the current forecast. Those operational gains could amplify the boost lower interest rates could deliver to storage transaction activity. While the national average cap rate on 2023 trades of 6.5 percent is the highest in five years, the margin relative to financing costs has narrowed some. Lower borrowing costs could enable more properties to change hands, further facilitating price discovery. The average sale price last year was $138 per square foot, down from 2022’s peak of $155 per square foot, but still up 30 percent from the pre-pandemic mark. As such, long-term owners can still capture ample appreciation, while still adjusting to current market dynamics that place upward pressure on cap rates.
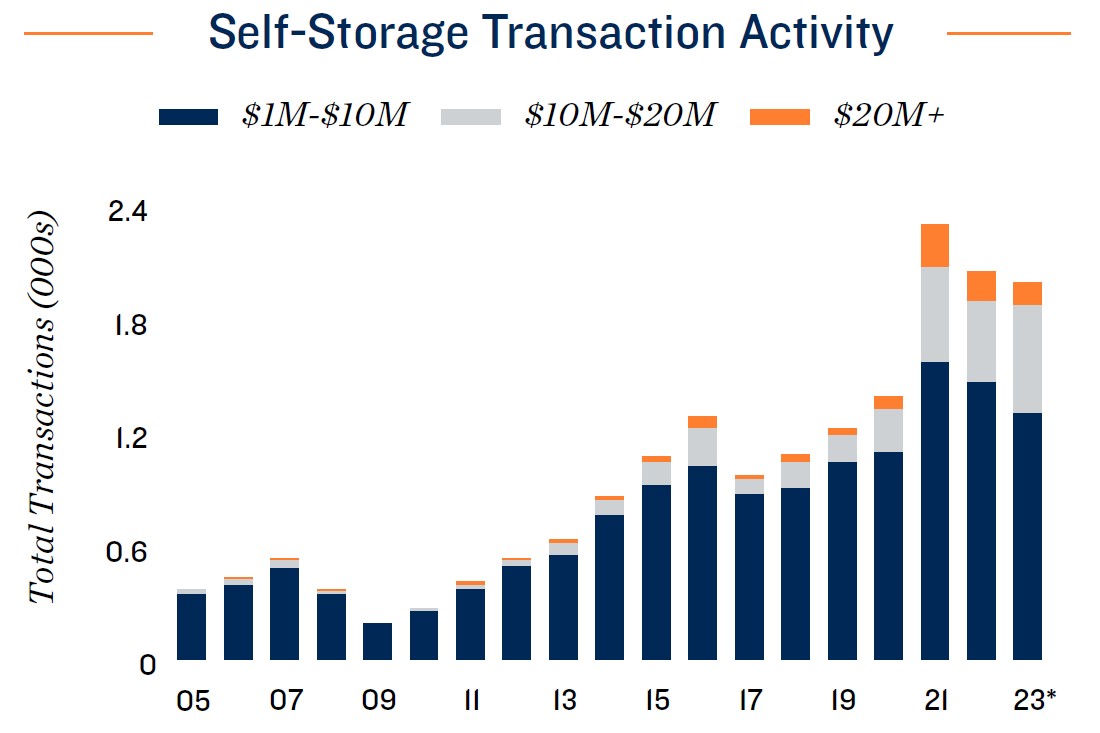
2024 INVESTMENT OUTLOOK
- Consolidation likely to continue. The sector saw multiple headline mergers in 2023, such as Extra Space Storage’s all-stock purchase of Life Storage, followed by Public Storage’s acquisition of Simply Self Storage later in the year. The largest operators will likely continue to seek pathways to growth through acquisitions and mergers as they continue to drive market penetration, coverage and economies of scale.
- Growth of third-party management services aids smaller operators. As the sector transitions from its small-business roots, a number of firms have risen to aid prospective owners with the daily operations of running a storage business. Partnering with an experienced manager can both ease the financing process during acquisition, and help stabilize facility operations afterward.
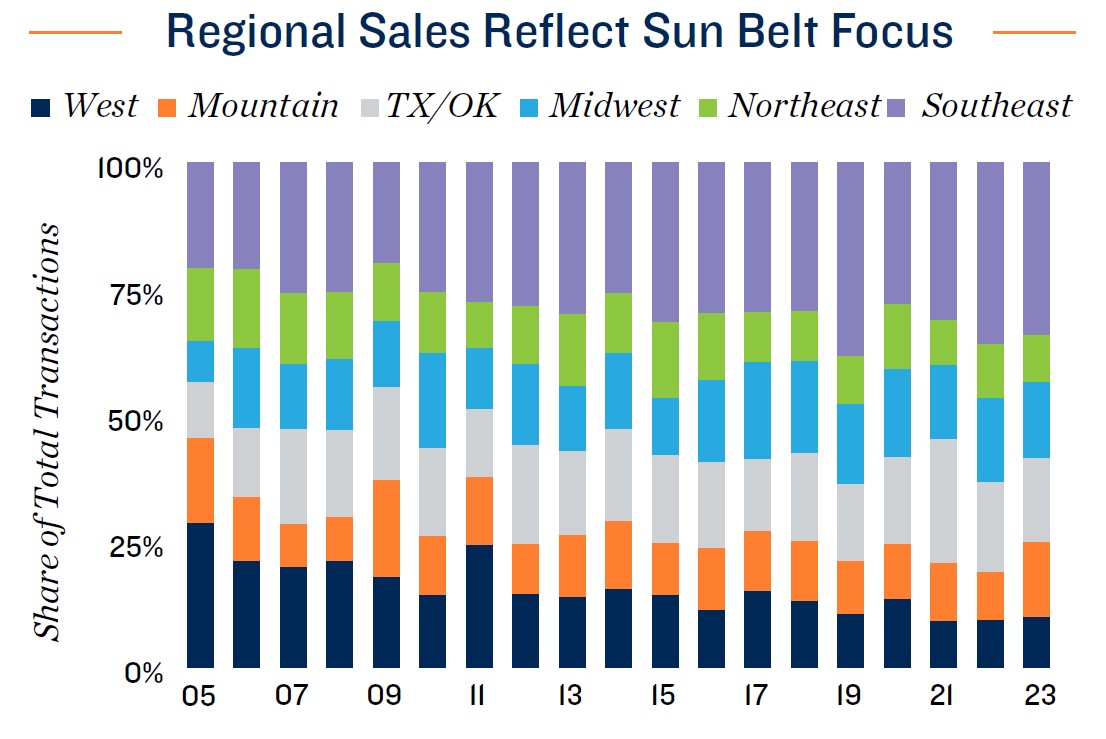
- Rocky Mountain and Southeast metros gain attention. Over the last 20 years, the distribution of self-storage investment sales has shifted more toward the Rocky Mountain and Southeast regions. Population migration, and the resulting impact on storage rental demand, is driving the shift. Robust development over the past five years has also created options for acquisitions of recently-built product.
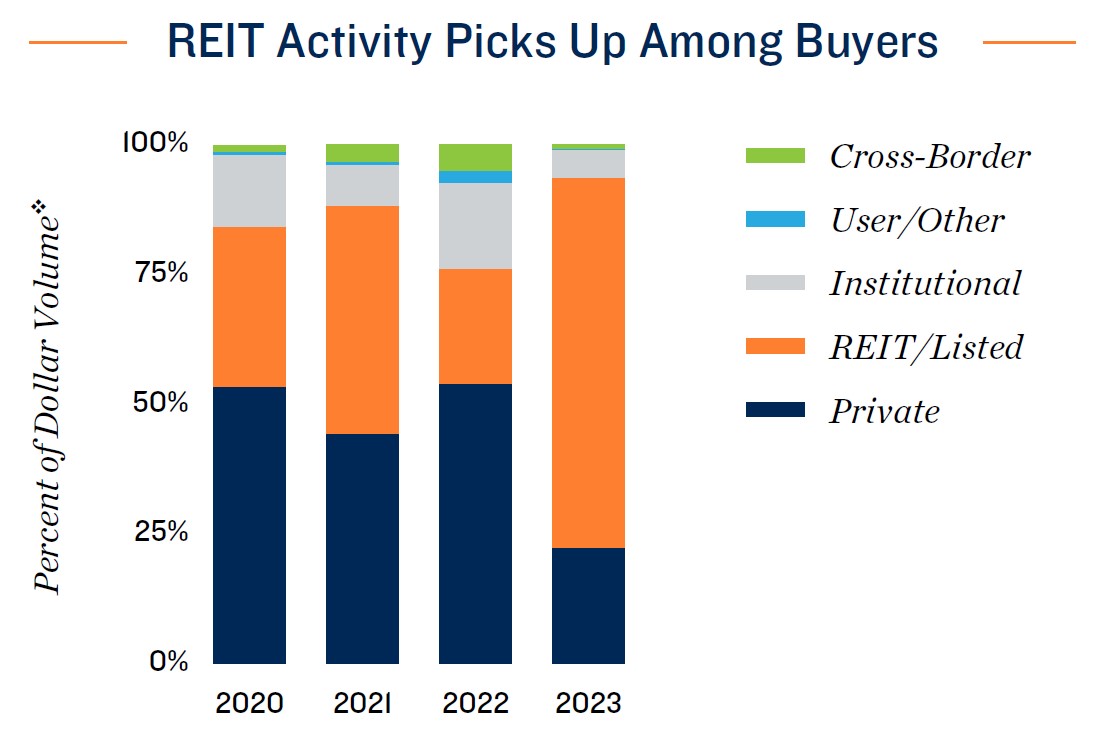
*Estimate
*Sales $2.5 million and greater
NATIONAL CONSTRUCTION TRENDS
DEVELOPMENT ELEVATED IN SOME MARKETS, SLOWING IN OTHERS
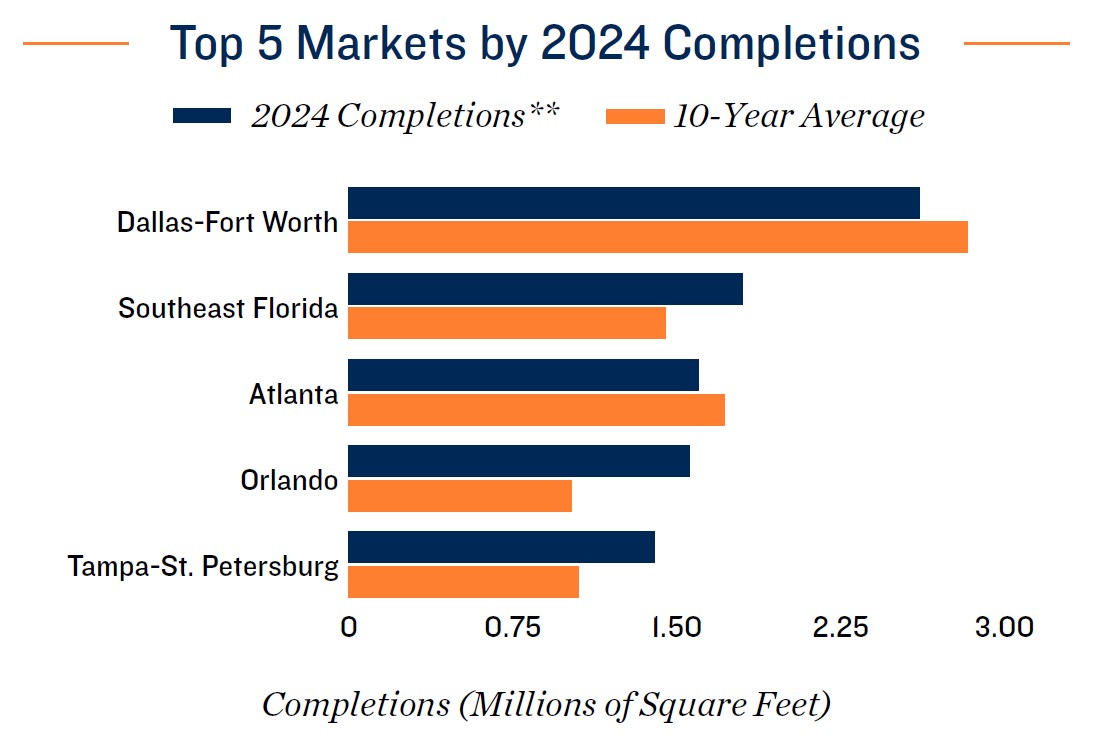
Construction trends downward, but story is nuanced by region. While self-storage operators are most concerned about competition on a localized basis, builders and lenders are more hesitant to break ground on projects in metros with weighty pipelines, mitigating the risks of oversupply. Although this is slowing inventory expansion on a national basis, some Sun Belt locales remain hotbeds for construction. Florida continues to be a development hotspot, with all of the state’s major metros expected to see development accelerate in 2024. This new stock could place acute pressure on street rates and vacancy, particularly in Tampa-St. Petersburg and Orlando, which boast some of the highest square foot per capita metrics nationwide. Development could taper cross the state moving forward, however, as insurance hurdles may impact inbound migration. Developers may begin to look toward more supply-constrained metros moving forward, where a lack of available parcels has traditionally inhibited development.
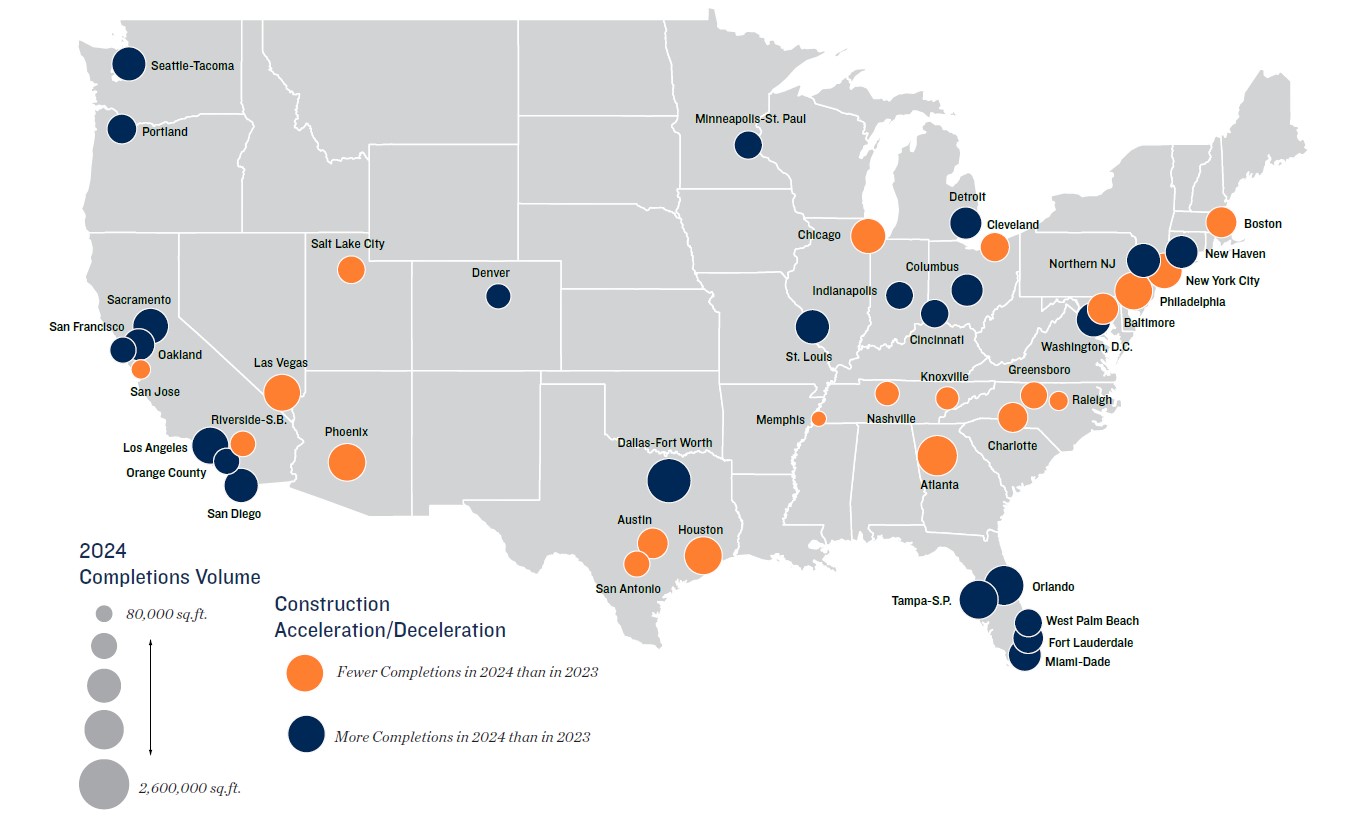
Primary markets and growing secondary metros divergent. New York City continues to boast the highest average street rate nationwide. Continued rent growth, despite heavy construction in recent years, indicates that densely-populated gateway metros like New York can sustain rapid supply increases. Builders are also increasing activity in the city’s bedroom communities in Northern New Jersey and Southwestern Connecticut, noting robust and consistent demand from an affluent suburban clientele. Nevertheless, most metros in North Carolina, Tennessee, and the Rocky Mountain region, which saw a bevy of new residents in the post-pandemic era, are seeing falling construction for 2024 in line with national trends. Many of these metros, such as Nashville, Raleigh and Salt Lake City, are also particularly exposed to Silicon Valley headwinds, due to the tech hubs in these areas. Such metros still offer long-term growth potential, however, as in-migration should continue at an above-average pace across most of these markets.
2024 Completions are forecast values
Sources: Marcus & Millichap Research Services; Yardi Matrix
HOUSING COST & DEMOGRAPHIC TRENDS
TIGHT HOUSING MARKET, AGING POPULATION SPELL FUTURE OF STORAGE DEMAND
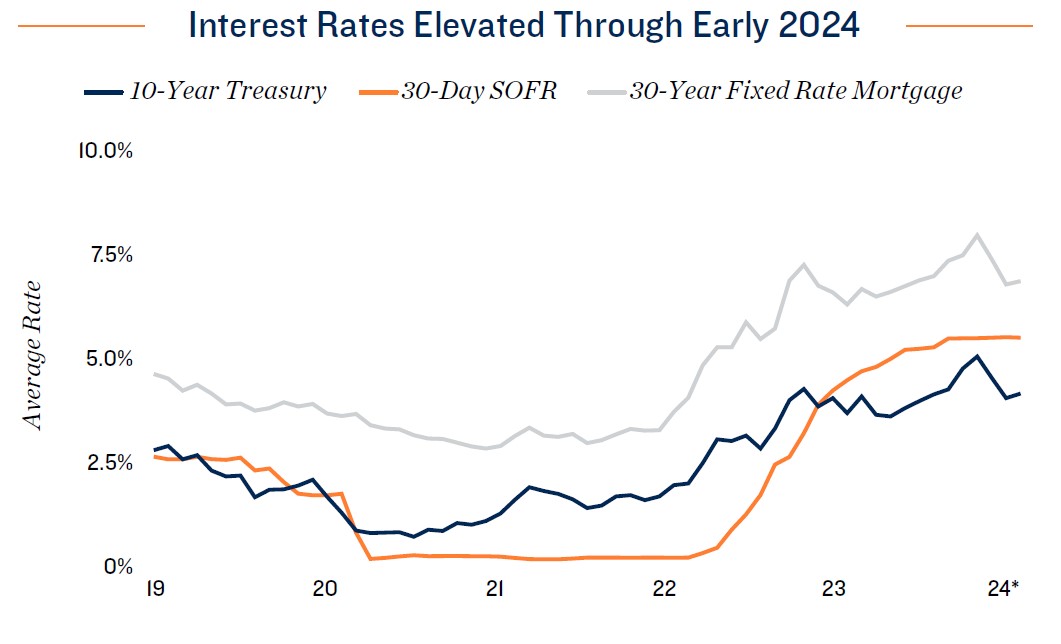
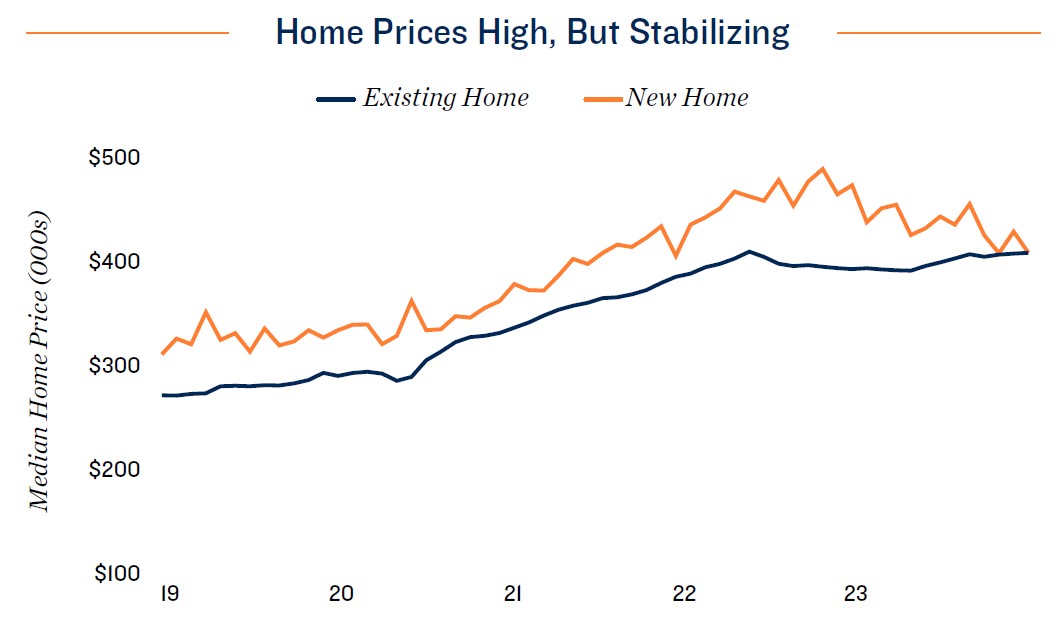
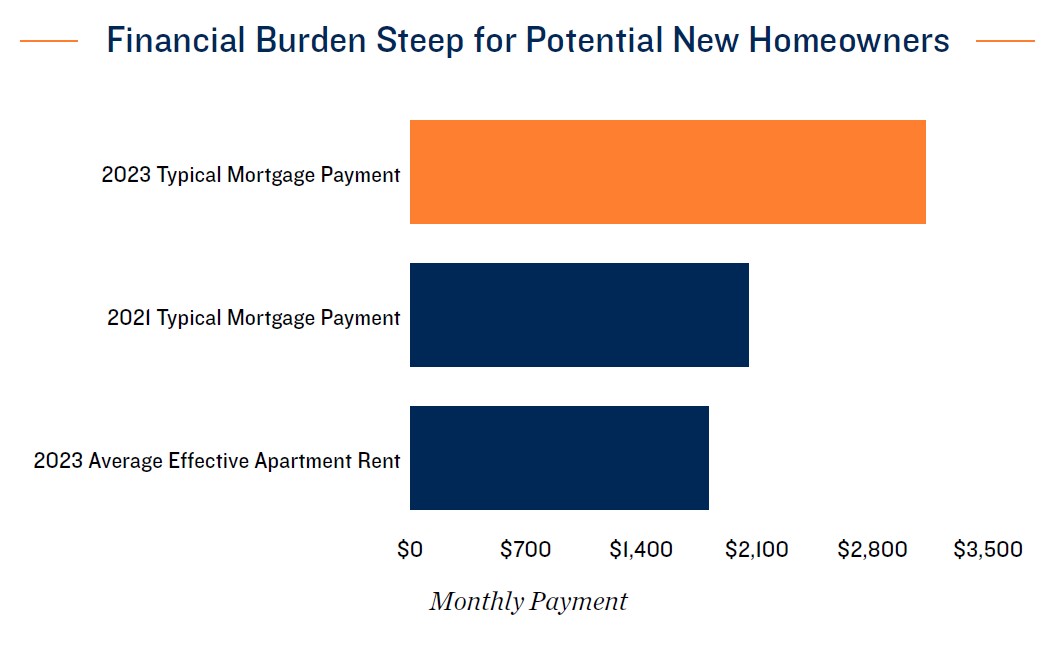
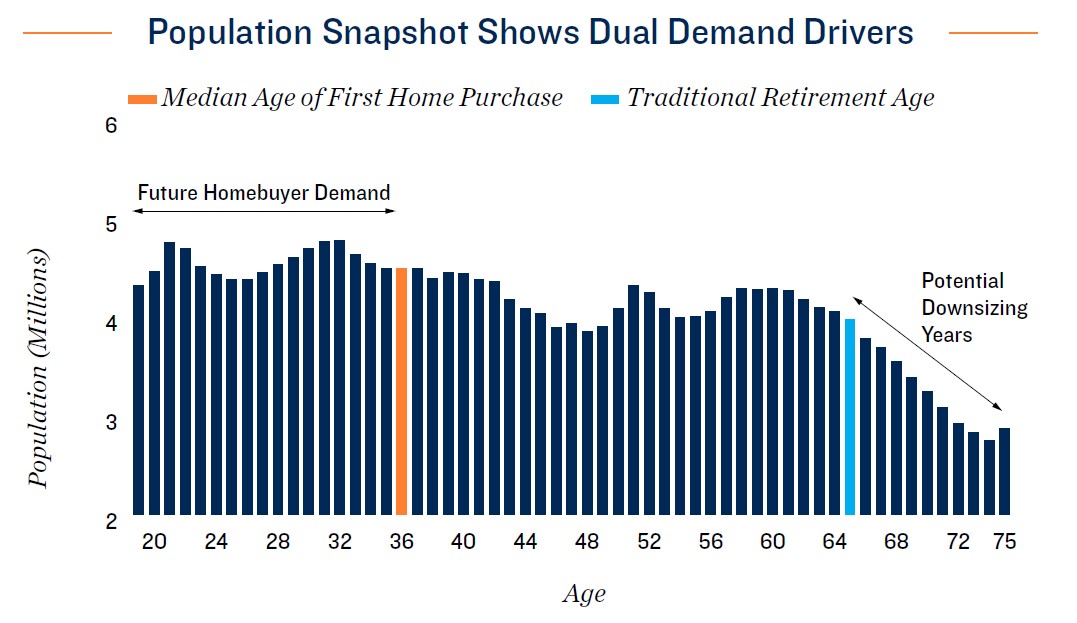
- The rapid increase of interest rates since March 2022 has had a dramatic impact on the housing market. The typical mortgage payment on a home priced at the U.S. median was over $3,100 at the start of 2024, up roughly 50 percent from two years prior. This comes amid a wave of baby boomers reaching retirement age, a period that typically accompanies downsizing into smaller living accommodations.
- Low for-sale home inventory and a $1,300 difference between the typical monthly mortgage payment and mean effective apartment rent is also delaying homeownership for millennial and older Gen Z renters. Much like their baby boomer counterparts, these residents find themselves locked in to current living arrangements. Monetary policy shifts could translate to some relief later in the year, however.
- Many older homeowners are waiting for interest rates to decline before searching for new abodes, keeping a large amount of single-family stock off the market. This has also kept home prices elevated, solidifying the barrier to homeownership for many prospective buyers, and limiting household formations and relocations, which can drive self-storage use. Nevertheless, these effects are not limited to older generations.
- The Federal Reserve is widely anticipated to lower interest rates at some point in 2024, which should unlock some pent-up homebuying demand across multiple age demographics. Still, evolving macroeconomic developments will determine the schedule and magnitude of any rate decreases, and policy lags may delay the full impact of loosening policy on the housing market, and subsequently self-storage demand.
Notes: Typical mortgage payment based on quarterly median home price for a 30-year fixed rate mortgage,
90% LTV, taxes, insurance and PMI.
* As of January
Sources: Marcus & Millichap Research Services; Federal Reserve Freddie Mac; Moody’s Analytics; Mortgage
Bankers Association; National Association of Home Builders; National Association of Realtors;
RealPage, Inc.; U.S. Census Bureau
